LeishVet Factsheets
Discover the new canine and feline LeishVet factsheets.
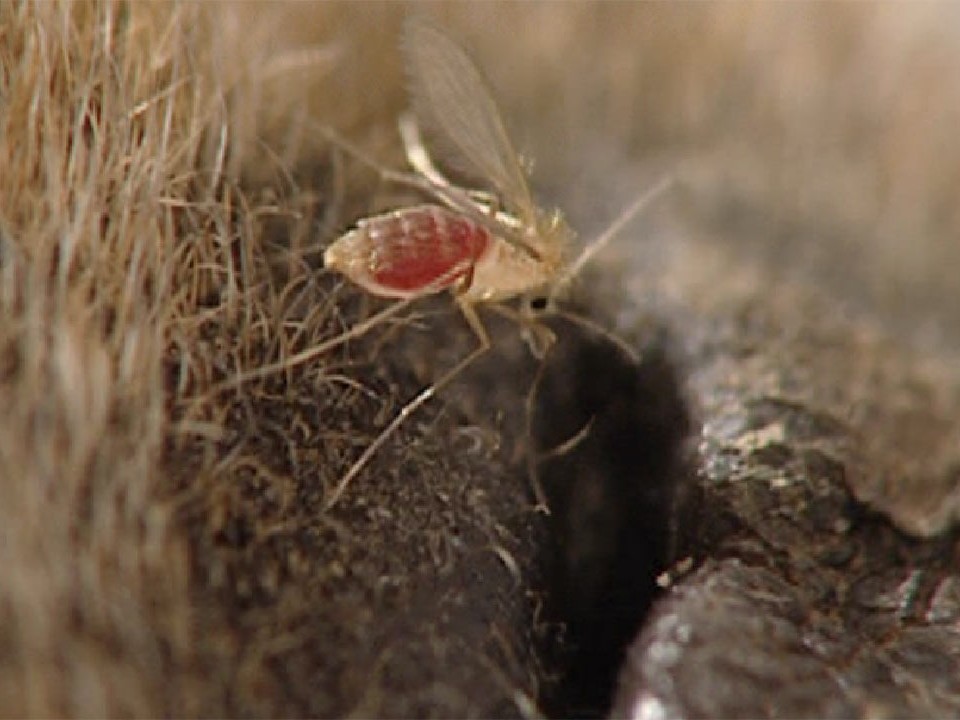
Etiology and Epidemiology (Distribution, Transmission)
Leishmania infections in dogs are predominantly due to Leishmania infantum.
Clinical Staging, Treatment and Prognosis
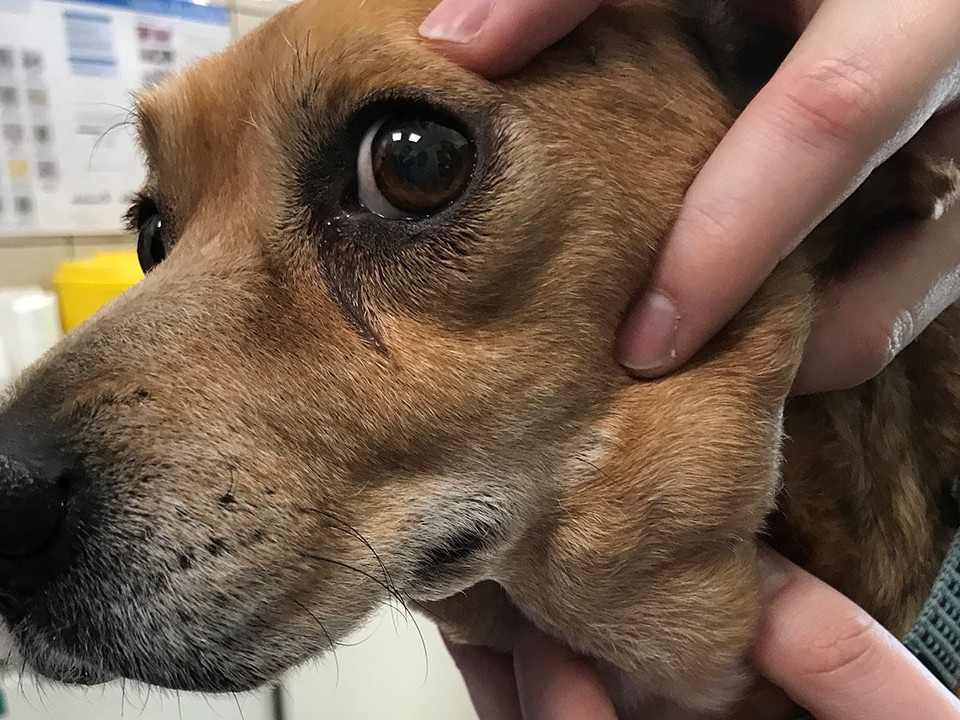
Staging is performed following canine patient diagnosis of L. infantum infection with clinical signs...
Prevention
Prevention for individual dogs (healthy, infected clinically healthy and sick) should always include use of a topical insecticide ...
Etiology, Geographic Distribution and Transmission
Cats are potentially infected by the same Leishmania spp. that infect dogs and humans in endemic areas all over the world...
Prevalence of Infection and Coinfections
Most information regarding feline L. infantum infection has come from investigations...
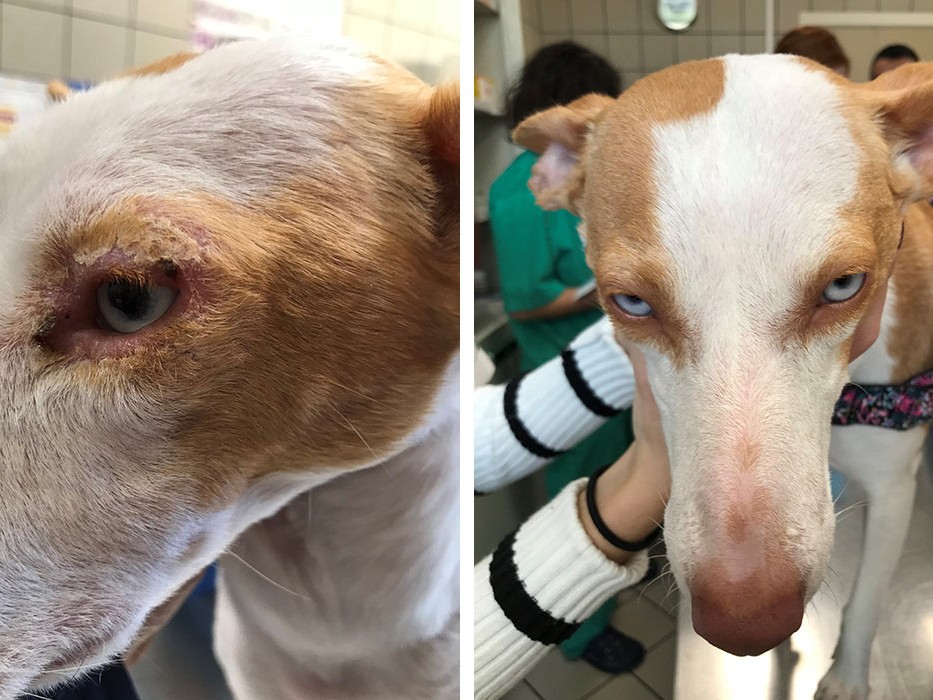
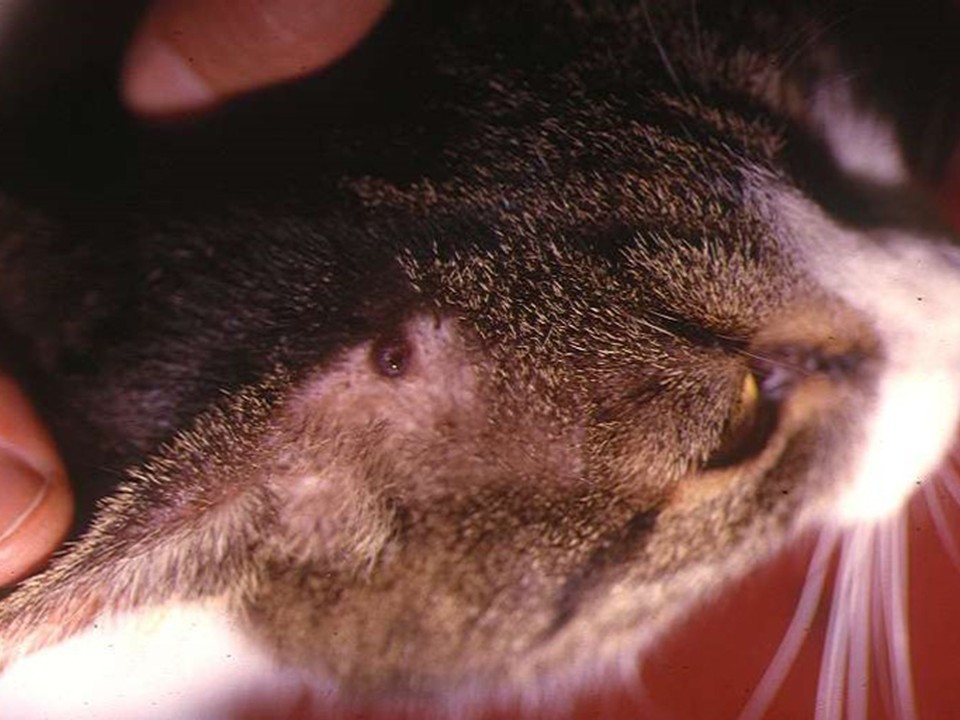
Leishmaniosis in Cats
Most FeL case reports are from European and Mediterranean endemic areas where the number of pet cats is high.
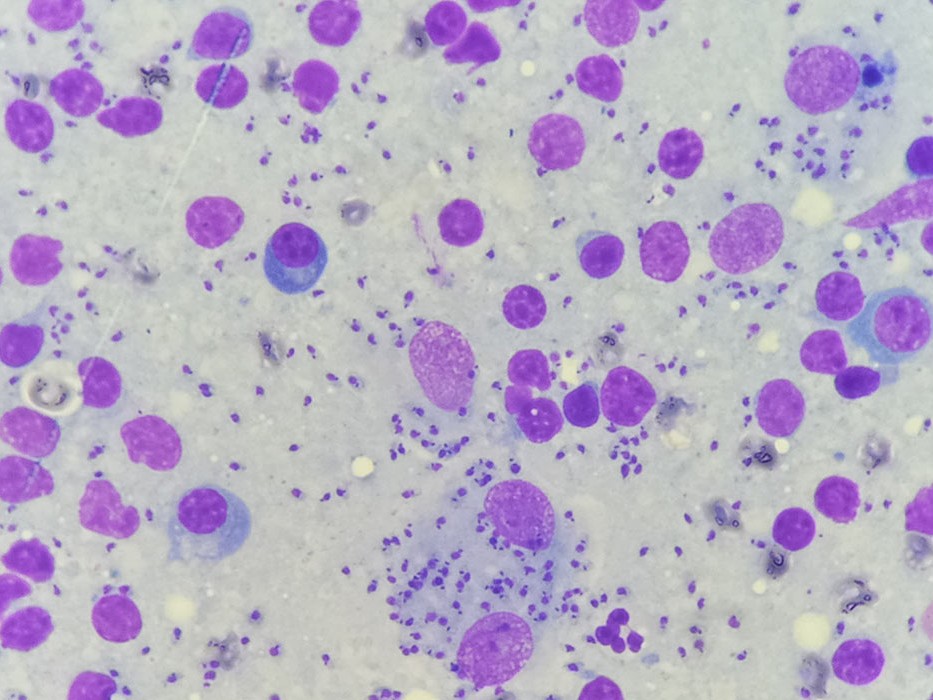
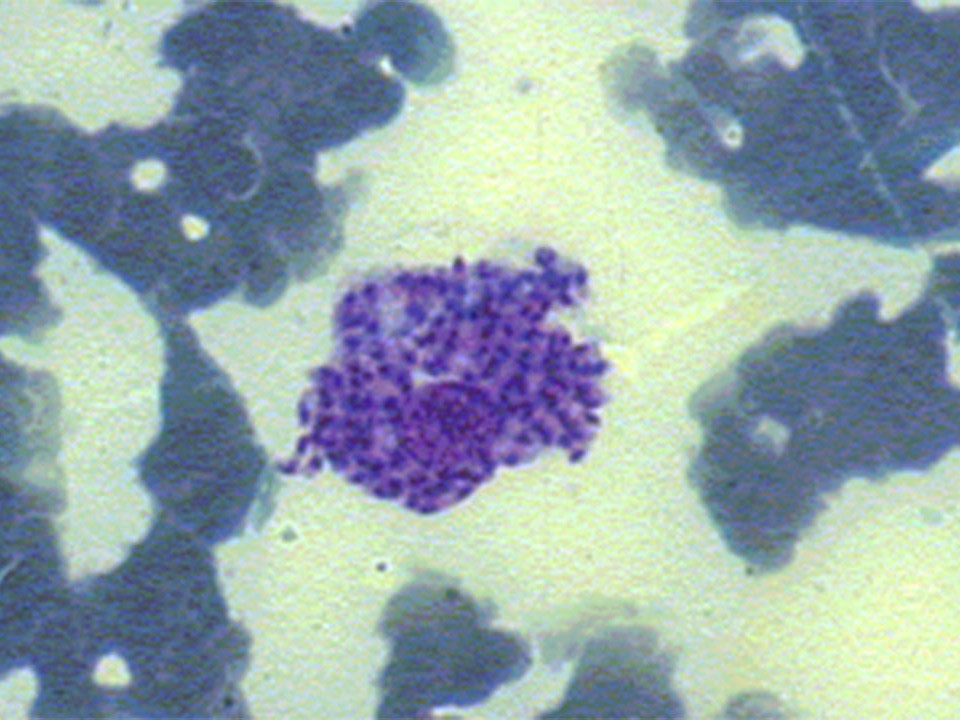
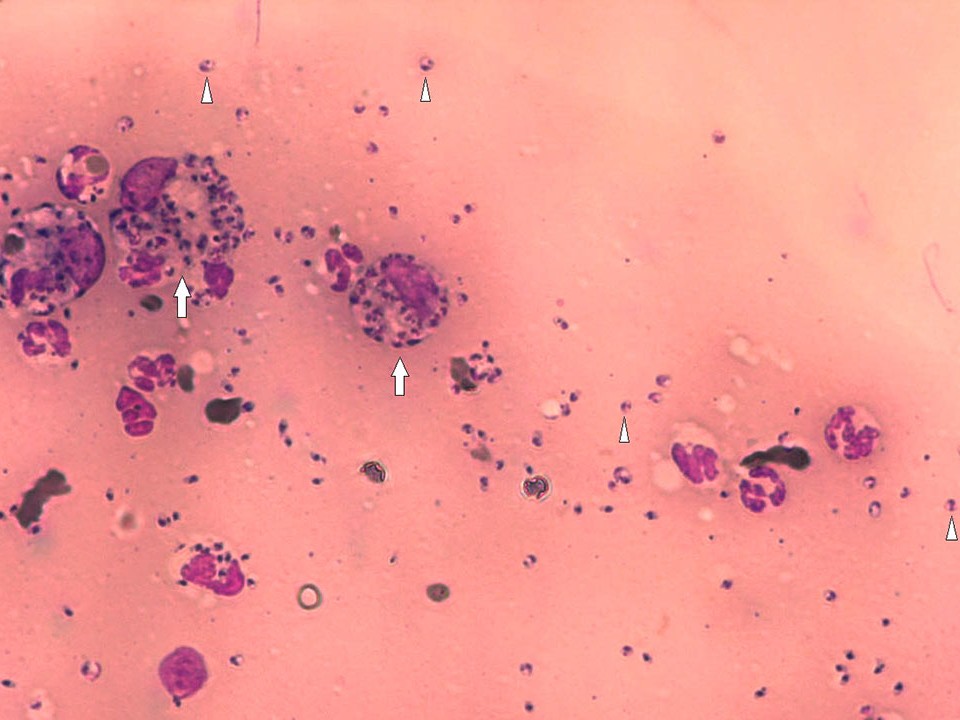
Purposes of Diagnosis
Confirm the etiology of disease in cats with clinical signs and/or clinicopathological abnormalities compatible with FeL
Clinically Healthy Infected Cats
Clinically healthy infected cats are antibody-positive (and/or PCR-positive) cats with no clinical signs...
Monitoring and Prognosis
Relapse of disease is frequently observed after the end of anti-Leishmania treatment. Clinical signs and/or...
Prevention and Key Points
In endemic areas, general prevention of sand fly bites is based on the same procedures as for dogs.